
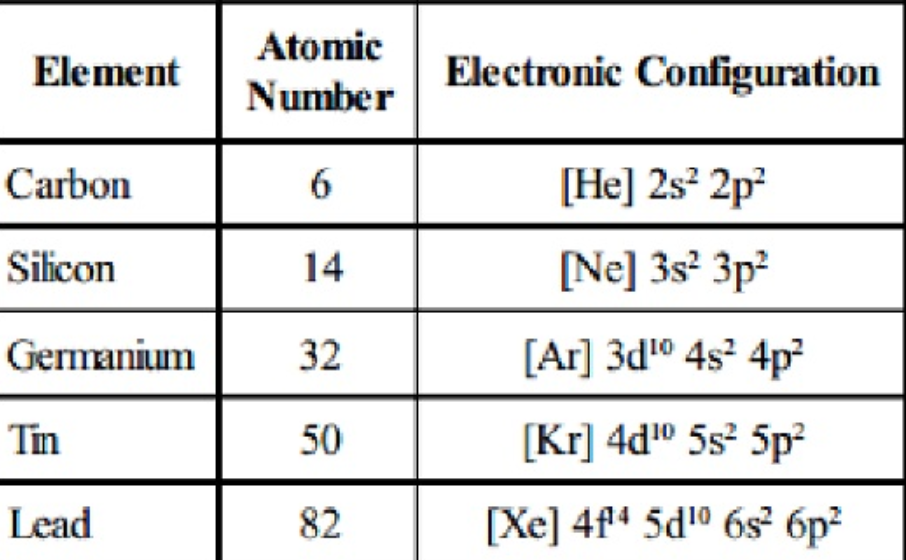
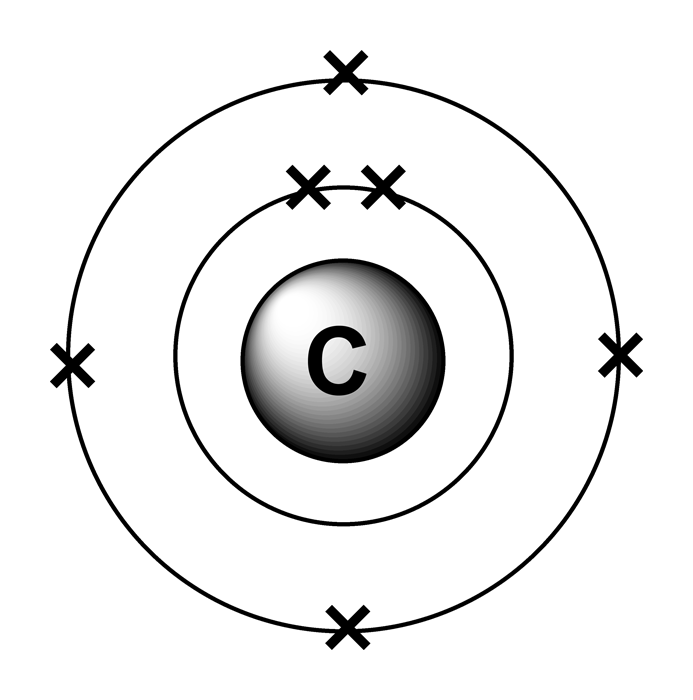
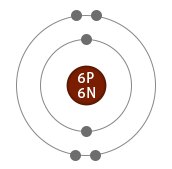
The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. Since the number of electrons and their arrangement are responsible for the chemical behavior of atoms, the atomic number identifies the various chemical elements. Each electron is influenced by the electric fields produced by the positive nuclear charge and the other (Z – 1) negative electrons in the atom. Therefore, the number of electrons in neutral atom of Carbon is 6. The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus. As a result, all living biological substances contain the same amount of C-14 per gram of carbon, that is 0.3 Bq of carbon-14 activity per gram of carbon. On average just one out of every 1.3 x 10 12 carbon atoms in the atmosphere is a radioactive carbon-14 atom. As a result, carbon-14 is continuously formed in the upper atmosphere by the interaction of cosmic rays with atmospheric nitrogen. Carbon-14 can also be produced in the atmosphere by other neutron reactions, including in particular 13C(n,γ)14C and 17O(n,α)14C. Radioactive carbon-14 has a half-life of 5730 years and undergoes β− decay, where the neutron is converted into a proton, an electron, and an electron antineutrino. The only cosmogenic radionuclide to make a significant contribution to internal exposure of human is carbon-14.
As one of the environmental isotopes, it makes up about 1.1% of all natural carbon on Earth. Carbon-12 is composed of 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons.Ĭarbon-13 is a natural, stable isotope of carbon with a nucleus containing six protons and seven neutrons. Carbon-12 is of particular importance in its use as the standard from which atomic masses of all nuclides are measured, thus, its atomic mass is exactly 12 daltons by definition. The longest-lived radioisotope is 14C, with a half-life of 5,730 years.Ĭarbon-12 is the more abundant of the two stable isotopes of carbon (carbon-13 being the other), amounting to 98.93% of the element carbon. Main Isotopes of CarbonĬarbon has 15 known isotopes, from 8C to 22C, of which 12C and 13C are stable.
Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Carbon are 12 13. Isotopes are nuclides that have the same atomic number and are therefore the same element, but differ in the number of neutrons. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.įor stable elements, there is usually a variety of stable isotopes.
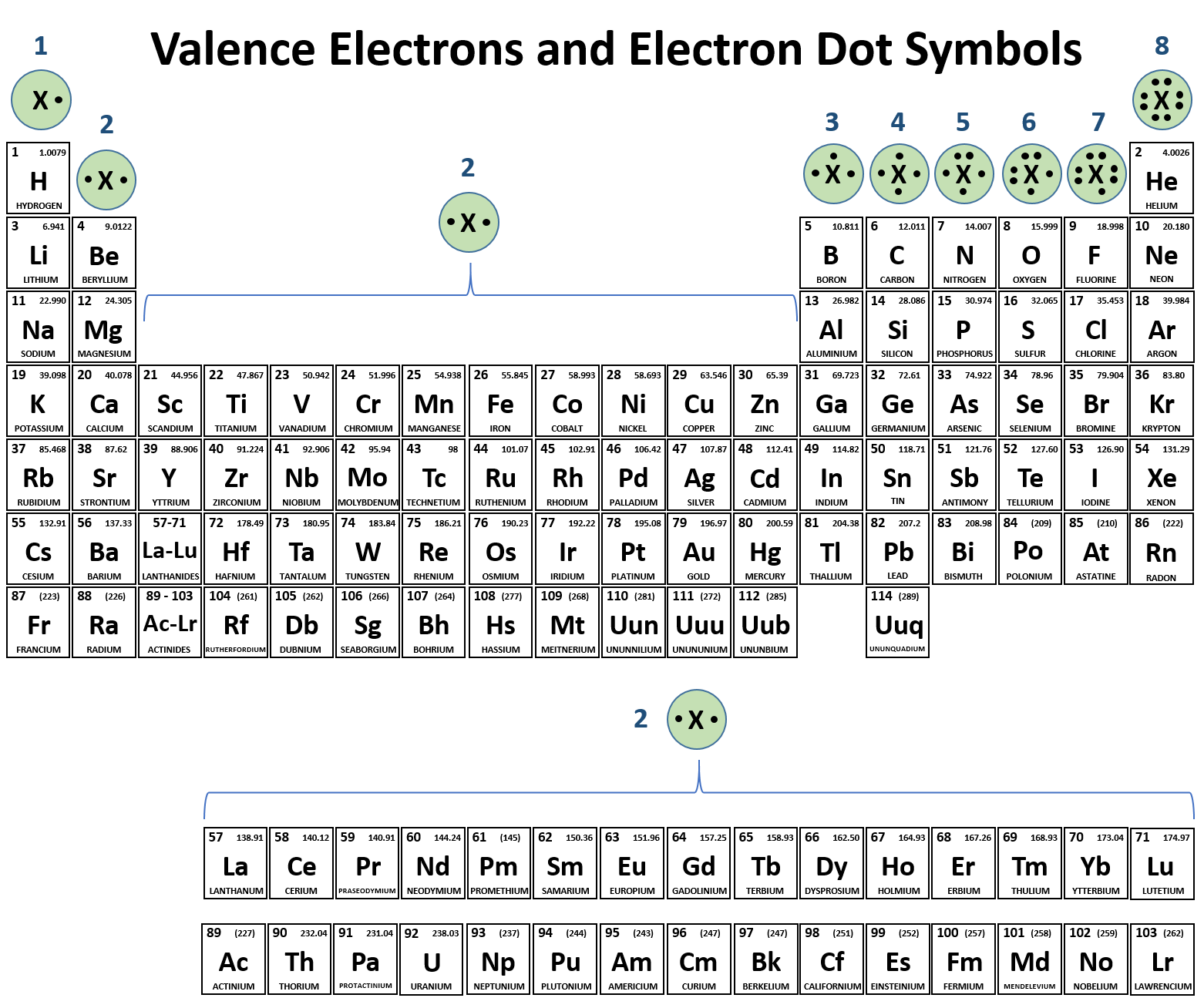
Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A. The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10 -19 coulombs. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. Carbon is a chemical element with atomic number 6 which means there are 6 protons in its nucleus.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
